所谓IO,也就是Input与Output的缩写。在java中,IO涉及的范围比较大,这里主要讨论针对文件内容的读写
其他知识点将放置后续章节(我想,文章太长了,谁都没耐心翻到最后)
?
对于文件内容的操作主要分为两大类
分别是:
字符流
字节流
其中,字符流有两个抽象类:Writer ??Reader
其对应子类FileWriter和FileReader可实现文件的读写操作
BufferedWriter和BufferedReader能够提供缓冲区功能,用以提高效率
?
同样,字节流也有两个抽象类:InputStream???OutputStream
其对应子类有FileInputStream和FileOutputStream实现文件读写
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream提供缓冲区功能
?
俺当初学IO的时候犯了不少迷糊,网上有些代码也无法通过编译,甚至风格都很大不同,所以新手请注意:? ? ? ?
??????? 1.本文代码较长,不该省略的都没省略,主要是因为作为一个新手需要养成良好的代码编写习惯
2.本文在linux下编译,类似于File.pathSeparator和File.separator这种表示方法是出于跨平台性和健壮性考虑
3.代码中有些操作有多种执行方式,我采用了方式1...方式2...的表述,只需轻轻解开注释便可编译
4.代码中并没有在主方法上抛出异常,而是分别捕捉,造成代码过长,如果仅是测试,或者不想有好的编程习惯,那你就随便抛吧……
??????? 5.功能类似的地方就没有重复写注释了,如果新手看不懂下面的代码,那肯定是上面的没有理解清楚
?
monospace !important; font-size: 12px !important; color: #0000ff !important;" class="java keyword">import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileWriter;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
?????????
????????//创建要操作的文件路径和名称
????????//其中,File.separator表示系统相关的分隔符,Linux下为:/? Windows下为:\\
????????String path = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?????
????????//由于IO操作会抛出异常,因此在try语句块的外部定义FileWriter的引用
????????FileWriter w = null;
????????try?{
????????????//以path为路径创建一个新的FileWriter对象
????????????//如果需要追加数据,而不是覆盖,则使用FileWriter(path,true)构造方法
????????????w = new?FileWriter(path);
?????????????
????????????//将字符串写入到流中,\r\n表示换行想有好的
????????????w.write("Nerxious is a good boy\r\n");
????????????//如果想马上看到写入效果,则需要调用w.flush()方法
????????????w.flush();
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????//如果前面发生异常,那么是无法产生w对象的
????????????//因此要做出判断,以免发生空指针异常
????????????if(w != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????//关闭流资源,需要再次捕捉异常
????????????????????w.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
编译之后,在目录下面生成文件,并写入字符串
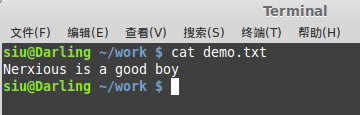
?
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileReader;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo2 {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
????????String path = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?
????????FileReader r = null;
????????try?{
????????????r = new?FileReader(path);
?????????????
????????????//方式一:读取单个字符的方式
????????????//每读取一次,向下移动一个字符单位
????????????int?temp1 = r.read();
????????????System.out.println((char)temp1);
????????????int?temp2 = r.read();
????????????System.out.println((char)temp2);
?????????????????????????
????????????//方式二:循环读取
????????????//read()方法读到文件末尾会返回-1
????????????/*
????????????while (true) {
????????????????int temp = r.read();
????????????????if (temp == -1) {
????????????????????break;
????????????????}
????????????????System.out.print((char)temp);
????????????}
????????????*/
?????????????
????????????//方式三:循环读取的简化操作
????????????//单个字符读取,当temp不等于-1的时候打印字符
????????????/*int temp = 0;
????????????while ((temp = r.read()) != -1) {
????????????????System.out.print((char)temp);
????????????}
????????????*/
?????????????
????????????//方式四:读入到字符数组
????????????/*
????????????char[] buf = new char[1024];
????????????int temp = r.read(buf);
????????????//将数组转化为字符串打印,后面参数的意思是
????????????//如果字符数组未满,转化成字符串打印后尾部也许会出现其他字符
????????????//因此,读取的字符有多少个,就转化多少为字符串
????????????System.out.println(new String(buf,0,temp));
????????????*/
?????????????
????????????//方式五:读入到字符数组的优化
????????????//由于有时候文件太大,无法确定需要定义的数组大小
????????????//因此一般定义数组长度为1024,采用循环的方式读入
????????????/*
????????????char[] buf = new char[1024];
????????????int temp = 0;
????????????while((temp = r.read(buf)) != -1) {
????????????????System.out.print(new String(buf,0,temp));
????????????}
????????????*/
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????if(r != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????r.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
编译之后的效果:
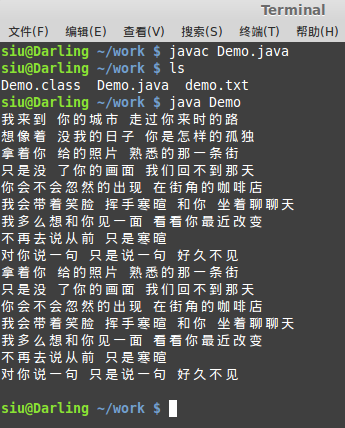
?
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileReader;
import?java.io.FileWriter;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
?????????
????????String doc = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?????????
????????String copy = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
?????????????????????File.separator + "life"?+ File.separator + "lrc.txt";
?
????????FileReader r = null;
????????FileWriter w = null;
????????try?{
????????????r = new?FileReader(doc);
????????????w = new?FileWriter(copy);
?????????????
????????????//方式一:单个字符写入
????????????int?temp = 0;
????????????while((temp = r.read()) != -1) {
????????????????w.write(temp);
????????????}
?????????????
????????????//方式二:字符数组方式写入
????????????/*
????????????char[] buf = new char[1024];
????????????int temp = 0;
????????????while ((temp = r.read(buf)) != -1) {
????????????????w.write(new String(buf,0,temp));
????????????}
????????????*/
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????//分别判断是否空指针引用,然后关闭流
????????????if(r != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????r.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????????if(w != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????w.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
?编译之后,产生life目录下的lrc.txt文件,复制成功
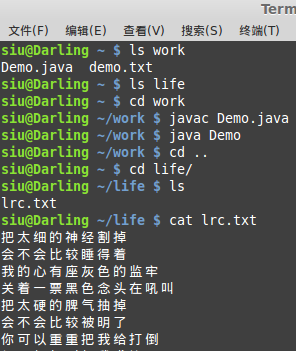
?
import?java.io.BufferedReader;
import?java.io.BufferedWriter;
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileReader;
import?java.io.FileWriter;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
?????????
????????String doc = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?????????
????????String copy = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
?????????????????????File.separator + "life"?+ File.separator + "lrc.txt";
?
????????FileReader r = null;
????????FileWriter w = null;
????????//创建缓冲区的引用
????????BufferedReader br = null;
????????BufferedWriter bw = null;
????????try?{
????????????r = new?FileReader(doc);
????????????w = new?FileWriter(copy);
????????????//创建缓冲区对象
????????????//将需要提高效率的FileReader和FileWriter对象放入其构造函数内
????????????//当然,也可以使用匿名对象的方式 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(doc));
????????????br = new?BufferedReader(r);
????????????bw = new?BufferedWriter(w);
?????????????
????????????String line = null;
????????????//读取行,直到返回null
????????????//readLine()方法只返回换行符之前的数据
????????????while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
????????????????//使用BufferWriter对象的写入方法
????????????????bw.write(line);
????????????????//写完文件内容之后换行
????????????????//newLine()方法依据平台而定
????????????????//windows下的换行是\r\n
????????????????//Linux下则是\n
????????????????bw.newLine();
????????????}??????
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????//此处不再需要捕捉FileReader和FileWriter对象的异常
????????????//关闭缓冲区就是关闭缓冲区中的流对象
????????????if(br != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????r.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????????if(bw != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????bw.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
?
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileOutputStream;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
??????????
????????String path = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?????????
????????FileOutputStream o = null;
?????????
????????try?{
????????????o = new?FileOutputStream(path);
????????????String str = "Nerxious is a good boy\r\n";
????????????byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
????????????//也可以直接使用o.write("String".getBytes());
????????????//因为字符串就是一个对象,能直接调用方法
????????????o.write(buf);
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????if(o != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????o.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????
????}
}
编译之后产生的文件,以上在字符串中加\r\n就是为了便于终端显示
其实在linux下面换行仅用\n即可
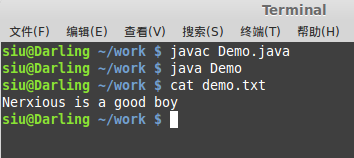
?
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileInputStream;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
??????????
????????String path = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "demo.txt";
?????????
????????FileInputStream i = null;
?????????
????????try?{
????????????i = new?FileInputStream(path);
?????????????
????????????//方式一:单个字符读取
????????????//需要注意的是,此处我用英文文本测试效果良好
????????????//但中文就悲剧了,不过下面两个方法效果良好
????????????int?ch = 0;
????????????while((ch=i.read()) != -1){
????????????????System.out.print((char)ch);
????????????}
?????????????
????????????//方式二:数组循环读取
????????????/*
????????????byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
????????????int len = 0;
????????????while((len = i.read(buf)) != -1) {
????????????????System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
????????????}
????????????*/
?????????????
?????????????
????????????//方式三:标准大小的数组读取
????????????/*
????????????//定一个一个刚好大小的数组
????????????//available()方法返回文件的字节数
????????????//但是,如果文件过大,内存溢出,那就悲剧了
????????????//所以,亲们要慎用!!!上面那个方法就不错
????????????byte[] buf = new byte[i.available()];
????????????i.read(buf);
????????????//因为数组大小刚好,所以转换为字符串时无需在构造函数中设置起始点
????????????System.out.println(new String(buf));
????????????*/
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????if(i != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????i.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????
????}
}
?读取文件到终端

?
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileInputStream;
import?java.io.FileOutputStream;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
??????????
????????String bin = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "一个人生活.mp3";
?????????
????????String copy = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "life"?+ File.separator + "一个人生活.mp3";
?????????
????????FileInputStream i = null;
????????FileOutputStream o = null;
?????????
????????try?{
????????????i = new?FileInputStream(bin);
????????????o = new?FileOutputStream(copy);
?????????????
????????????//循环的方式读入写出文件,从而完成复制
????????????byte[] buf = new?byte[1024];
????????????int?temp = 0;
????????????while((temp = i.read(buf)) != -1) {
????????????????o.write(buf, 0, temp);
????????????}
?
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????if(i != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????i.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????????if(o != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????o.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
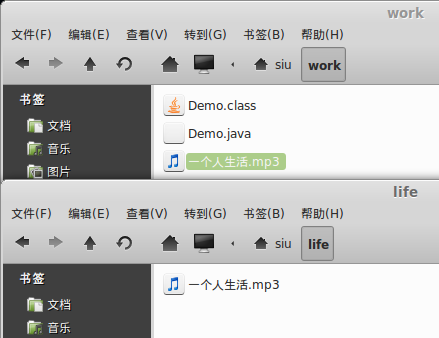
?复制效果,如图:
import?java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import?java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import?java.io.File;
import?java.io.FileInputStream;
import?java.io.FileOutputStream;
import?java.io.IOException;
?
public?class?Demo {
????public?static?void?main(String[] args ) {
??????????
????????String bin = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "work"?+ File.separator + "一个人生活.mp3";
?????????
????????String copy = File.separator + "home"?+ File.separator + "siu"?+
??????????????????????File.separator + "life"?+ File.separator + "一个人生活.mp3";
?????????
????????FileInputStream i = null;
????????FileOutputStream o = null;
????????BufferedInputStream bi = null;
????????BufferedOutputStream bo = null;
?????????
????????try?{
????????????i = new?FileInputStream(bin);
????????????o = new?FileOutputStream(copy);
????????????bi = new?BufferedInputStream(i);
????????????bo = new?BufferedOutputStream(o);
?????????????
????????????byte[] buf = new?byte[1024];
????????????int?temp = 0;
????????????while((temp = bi.read(buf)) != -1) {
????????????????bo.write(buf,0,temp);
????????????}
?????????????
????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????} finally?{
????????????if(bi != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????i.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????????if(bo != null) {
????????????????try?{
????????????????????o.close();
????????????????} catch?(IOException e) {
????????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????????}
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
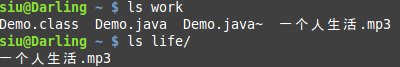
?两个目录都有 “一个人生活.mp3”文件,顺便说一下,这歌挺好听的
?
初学者在学会使用字符流和字节流之后未免会产生疑问:什么时候该使用字符流,什么时候又该使用字节流呢?
其实仔细想想就应该知道,所谓字符流,肯定是用于操作类似文本文件或者带有字符文件的场合比较多
而字节流则是操作那些无法直接获取文本信息的二进制文件,比如图片,mp3,视频文件等
说白了在硬盘上都是以字节存储的,只不过字符流在操作文本上面更方便一点而已
此外,为什么要利用缓冲区呢?
我们知道,像迅雷等下载软件都有个缓存的功能,硬盘本身也有缓冲区
试想一下,如果一有数据,不论大小就开始读写,势必会给硬盘造成很大负担,它会感觉很不爽
人不也一样,一顿饭不让你一次吃完,每分钟喂一勺,你怎么想?
因此,采用缓冲区能够在读写大文件的时候有效提高效率