学习EF之前要熟悉以下知识:
1.自动属性(Auto-Implemented Properties)
//以前的写法 private string _userName; public string UserName { get { return _userName; } set { _userName= value; } } //现在 public string_userName {get;set;}
2.隐式类型var
它是在编译已经能确定变量的类型,是根据后面的值自动推断类型,编译时把推断的类型替换掉var
看如下代码: var v = new { Name="Tom",Age="18",Email="Tom@163.com" }; Console.WriteLine(v.Name); Console.WriteLine(v.Age); Console.WriteLine(v.Email); Console.ReadLine();
//var v.Name=”小明” ,隐式类型只能读取,不能赋值
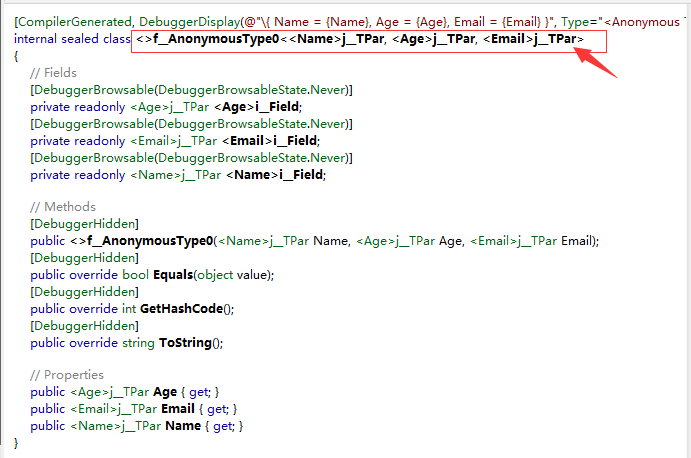
通过反编译我们看到编译器给我们自动生成了一个我们没见过的类,这就是隐式类型
3.对象初始化器与集合初始化器
对象初始化器
//写法一 DemoTest person = new DemoTest { Name="xiaoming",Age=18,Sex="boy"}; //写法一 DemoTest person = new DemoTest("123") { Name="xiaoming",Age=18,Sex="boy"}; //二种写法都在什么时候用? //写法一 是在调用类的默认构造函数时用 //写法二 是在调用类的默认有参构造函数时用
集合初始化器
List<DemoTest> list= new List<DemoTes> { new DemoTest(){ Age=18,Name="xiaoming",Sex="boy"}, new DemoTest(){ Age=19,Name="xiaohua",Sex="girl"} };
4.扩展方法
static void Main(string[] args) { List<string> list = new List<string>(); list.Contains//转到定义 }
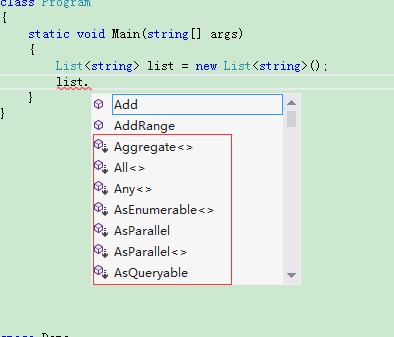
这些带向下箭头的都是扩展的,那么我们转到定义(f12)看下,这个扩展定义在Enumerable类里面,是不是跟大家想的不一样?一般都是转到List<T>本类里面,所以所有的扩展方法,都在静态类中。
我们要写扩展方法的主要目的是什么?
当一个类型已经写好之后,需要给这个类型加一些方法,但是加这个方法的时候不能修改类型,不能修改这个类的源代码,那么大家会想直接修改源代码不就行了,假如.net2.0以前的版本list有一些方法是一个版本,你要是修改了可能有不兼容的问题
下面我们就自己写一个扩展方法
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //给NewClass加个扩展方法 NewClass newclass = new NewClass(); newclass.Age = 18; newclass.ShowMessage(); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class NewClass { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); } } //1.创建一个静态类 public static class DemoTest { public static void ShowMessage(this NewClass newclass)//这里必须加this,不加就是普通的方法 { Console.WriteLine(newclass.Age); } }
下面我们给string加一个扩展方法:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string str = "Hello"; int result = str.GetLength(); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } //1.创建一个静态类 public static class DemoTest { public static int GetLength(this string str) { //扩展方法不能访问类型中私有成员 return str.Length; } }
接下来我们用反编译看下:
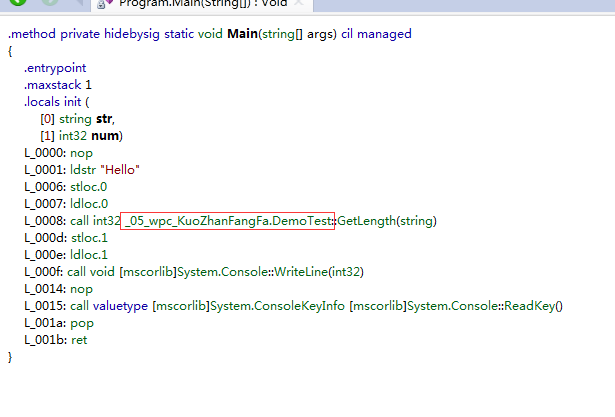
扩展方法只是看起来像是某个对象的方法,从反编译我们可以看出实际上根本不是该对象的方法,其实就是调用了某个静态类中的方法。
更多的请看:http://www.cnblogs.com/ldp615/archive/2009/08/07/1541404.html
5.Lambda表达式
首先我们说下匿名方法(知道即可),什么是匿名方法?我们写一个方法为什么要不写名字呢?那么我们该怎么调用呢?接下来就这些问题进行解答:
1.顾名思义,没有方法名的就叫匿名方法(O(∩_∩)O~)
2.当一个方法只用一次,不需要在用,所以没有必要在为方法起一个名字,这样做简单,方便
3.匿名方法不能直接定义,而是在给委托变量赋值一个方法时定义
定义匿名方法代码如下:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { DemoDelegate demoDelegate = delegate() { Console.WriteLine("O(∩_∩)O~"); }; demoDelegate(); ShowMessage(); Console.ReadKey(); } static void ShowMessage() { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); } } public delegate void DemoDelegate();//定义一个无参数无返回值的委托
那么接下来我们说下猪脚Lambda:Lambda其实就是匿名方法的简化写法
什么是Lambda表达式?'Lambda表达式'就是一个匿名的函数(匿名方法),可以包含表达式和语句,可创建委托
代码如下:
1.无参数无返回值
DemoDelegate demoLambda = () => { Console.WriteLine("我是Lambda表达式!"); }; demoLambda(); Console.ReadKey();
2.有参数有返回值
写法一:
static void Main(string[] args) { ParamsDelegate demoDelegate = (num1, str) => { return num1 + int.Parse(str); //也可以用Convert.ToInt32(obj)进行转换 反编译可以看下它其实调用的还是int.Parse(string) }; int result = demoDelegate(10,"10"); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } public delegate int ParamsDelegate(int num1, string str);//有参数有返回值
写法二:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ParamsDelegate paramsDelegate = (arr) => { for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(arr[i]); } return arr.Sum(); }; int result = paramsDelegate(1, 4, 5, 10, 9); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } public delegate int ParamsDelegate(params int[] arr);
Lambda其他用法:
首先扩展下泛型委托:
1.Action(非泛型版本)
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //保存无参数无返回值
Action action = new Action(Ac); action(); Console.ReadKey(); } static void Ac() { Console.WriteLine("Hello Action!"); } }
2.Action<>(泛型版本)
static void Main(string[] args) { //有多个参数,无返回值 Action<string> listAction = new Action<string>(ListAc);//也可以直接写ListAc listAction("Hello ListAction!"); //Lambda写法
Action<int,int> lambda=(num1,num2)=>{
Console.WriteLine(num1+num2);
};
lambda(5,10);
Console.ReadKey(); } static void ListAc(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); }
3.Func<>(只有泛型版本)
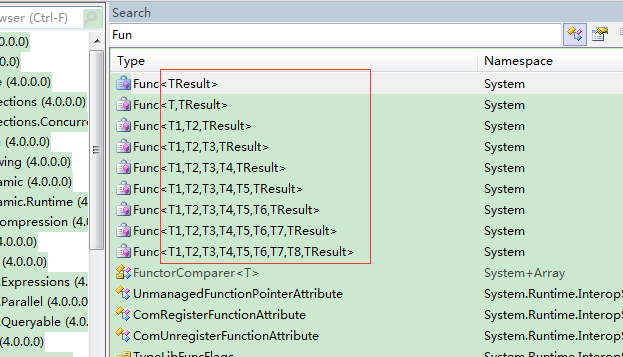
通过反编译可以看出,Func<>必须有返回值,可以有参数,用代码看下:
static void Main(string[] args) { //Func<int, int, int,int> listFunc = ListFunc; //int result = ListFunc(5, 10, 15); //Console.WriteLine(result); //Lambda写法 Func<int,int,int> func = (num1,num2) => { return num1+num2; }; int result=func(5,10); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } static int ListFunc(int num1,int num2,int num3) { return num1 + num2 + num3; }
我们看下常见筛选时使用lambda
List<int> list = new List<int>() {3,9,6,8,5,20,90,30,26,66}; IEnumerable<int> ie =list.Where(l => { return l > 10; }); foreach (var item in ie) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey();
结尾:第一次写博文,还请大神们多多指点!