客户端通信过程
1.通过SocketConnector同服务器端建立连接
2.链接建立之后I/O的读写交给了I/O Processor线程,I/O Processor是多线程的
3.通过I/O Processor读取的数据经过IoFilterChain里所有配置的IoFilter,IoFilter进行消息的过滤,格式的转换,在这个层面可以制定一些自定义的协议
4.最后IoFilter将数据交给Handler进行业务处理,完成了整个读取的过程
5.写入过程也是类似,只是刚好倒过来,通过IoSession.write写出数据,然后Handler进行写入的业务处理,处理完成后交给IoFilterChain,进行消息过滤和协议的转换,最后通过I/O Processor将数据写出到socket通道
IoFilterChain作为消息过滤链
1.读取的时候是从低级协议到高级协议的过程,一般来说从byte字节逐渐转换成业务对象的过程
2.写入的时候一般是从业务对象到字节byte的过程
IoSession贯穿整个通信过程的始终
整个过程可以用一个图来表现 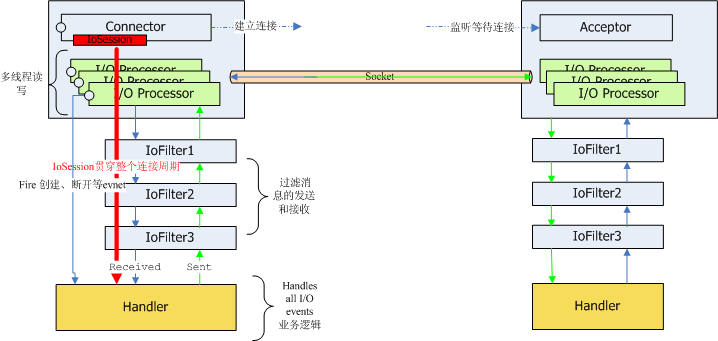
消息箭头都是有NioProcessor-N线程发起调用,默认情况下也在NioProcessor-N线程中执行
类图
http://mina.apache.org/class-diagrams.html#ClassDiagrams-ProtocolDecoderclassdiagram
Connector
作为连接客户端,SocketConector用来和服务器端建立连接,连接成功,创建IoProcessor Thread(不能超过指定的processorCount),Thread由指定的线程池进行管理,IoProcessor 利用NIO框架对IO进行处理,同时创建IoSession。连接的建立是通过Nio的SocketChannel进行。
NioSocketConnector connector = new NioSocketConnector(processorCount);
ConnectFuture future = connector.connect(new InetSocketAddress(HOSTNAME, PORT));建立一个I/O通道
Acceptor
作为服务器端的连接接受者,SocketAcceptor用来监听端口,同客户端建立连接,连接建立之后的I/O操作全部交给IoProcessor进行处理
IoAcceptor acceptor = new NioSocketAcceptor();
acceptor.bind( new InetSocketAddress(PORT) );
Protocol
利用IoFilter,对消息进行解码和编码,如以下代码通过 MyProtocolEncoder 将java对象转成byte串,通过MyProtocalDecoder 将byte串恢复成java对象
 ?
? spinner">
spinner">
connector.getFilterChain().addLast("codec", new ProtocolCodecFilter(new MyProtocalFactory()));
......
public class MyProtocalFactory implements ProtocolCodecFactory {
ProtocolEncoderAdapter encoder = new MyProtocolEncoder();
ProtocolDecoder decoder = new MyProtocalDecoder() ;
public ProtocolDecoder getDecoder(IoSession session) throws Exception {
return decoder;
}
public ProtocolEncoder getEncoder(IoSession session) throws Exception {
return encoder;
}
}
......
public class MyProtocalDecoder extends ProtocolDecoderAdapter {
public void decode(IoSession session, IoBuffer in, ProtocolDecoderOutput out)
throws Exception {
int id = in.getInt();
int len = in.getInt();
byte[] dst = new byte[len];
in.get(dst);
String name = new String(dst,"GBK");
Item item = new Item();
item.setId(id);
item.setName(name);
out.write(item);
}
}
......
public class MyProtocolEncoder extends ProtocolEncoderAdapter {
public void encode(IoSession session, Object message,
ProtocolEncoderOutput out) throws Exception {
Item item = (Item)message;
int byteLen = 8 + item.getName().getBytes("GBK").length ;
IoBuffer buf = IoBuffer.allocate(byteLen);
buf.putInt(item.getId());
buf.putInt(item.getName().getBytes("GBK").length);
buf.put(item.getName().getBytes("GBK"));
buf.flip();
out.write(buf);
}
}
handler
具体处理事件,事件包括:sessionCreated、sessionOpened、sessionClosed、sessionIdle、exceptionCaught、messageReceived、messageSent。
connector.setHandler(new MyHandler());MyHandler继承IoHandlerAdapter类或者实现IoHandler接口.事件最终由IoProcessor线程发动调用。
Processor
I/O处理器、允许多线程读写,开发过程中只需要指定线程数量,Processor通过Nio框架进行I/O的续写操作,Processor包含了Nio的Selector的引用。这点也正是mina的优势,如果直接用Nio编写,则需要自己编写代码来实现类似Processor的功能。正因为I/O Processor是异步处理读写的,所以我们有时候需要识别同一个任务的消息,比如一个任务包括发送消息,接收消息,反馈消息,那么我们需要在制定消息格式的时候,消息头里能包含一个能识别是同一个任务的id。
I/O Porcessor线程数的设置 :如果是SocketConnector,则可以在构造方法中指定,如:new SocketConnector(processorCount, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());如果是SocketAcceptor,也是一样的:SocketAcceptor acceptor = new SocketAcceptor(ProcessorCount, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
processorCount为最大Porcessor线程数,这个值可以通过性能测试进行调优,默认值是cpu核数量+1(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1)。
比较奇怪的是,每个IoProcessor在创建的时候会本地自己和自己建立一个连接?
IoSession
IoSession是用来保持IoService的上下文,一个IoService在建立Connect之后建立一个IoSession(一个连接一个session),IoSession的生命周期从Connection建立到断开为止
IoSession做两件事情:
1.通过IoSession可以获取IoService的所有相关配置对象(持有对IoService,Processor池,SocketChannel,SessionConfig和IoService.IoHandler的引用)
2.通过IoSession.write 是数据写出的入口
关于线程
http://mina.apache.org/configuring-thread-model.html
ThreadModel 1.x版本的mina还有线程模式选项在2.x之后就没有了
1.x版本指定线程模式
SocketConnectorConfig cfg = new SocketConnectorConfig();
cfg.setThreadModel(ThreadModel.MANUAL);
MINA有3种worker线程
Acceptor、Connector、I/O processor 线程
Acceptor Thread
一般作为服务器端链接的接收线程,实现了接口IoService,线程的数量就是创建SocketAcceptor 的数量
Connector Thread
一般作为客户端的请求建立链接线程,实现了接口IoService,维持了一个和服务器端Acceptor的一个链接,线程数量就是创建SocketConnector 的数量
Mina的SocketAcceptor和SocketConnector均是继承了BaseIoService,是对IoService的两种不同的实现
I/O processor Thread
作为I/O真正处理的线程,存在于服务器端和客户端,用来处理I/O的读写操作,线程的数量是可以配置的,默认最大数量是CPU个数+1
服务器端:在创建SocketAcceptor的时候指定ProcessorCount
SocketAcceptor acceptor = new SocketAcceptor(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
客户端:在创建SocketConnector 的时候指定ProcessorCount
SocketConnector connector = new SocketConnector(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
I/O Processor Thread,是依附于IoService,类似上面的例子SocketConnector connector = new SocketConnector(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());是指SocketConnector这个线程允许CPU+1个I/O Processor Thread
NioProcessor虽然是多线程,但是对与一个连接的时候业务处理只会使用一个线程进行处理(Processor线程对于一个客户端连接只使用一个线程NioProcessor-n)如果handler的业务比较耗时,会导致NioProcessor线程堵塞 ,在2个客户端同时连接上来的时候会创建第2个(前提是第1个NioProcessor正在忙),创建的最大数量由Acceptor构造方法的时候指定。如果:一个客户端连接同服务器端有很多通信,并且I/O的开销不大,但是Handler处理的业务时间比较长,那么需要采用独立的线程模式,在FilterChain的最后增加一个ExecutorFitler:
acceptor.getFilterChain().addLast("threadPool", new ExecutorFilter(Executors.newCachedThreadPool()));
这样可以保证processor和handler的线程是分开的,否则:客户端发送3个消息,而服务器对于每个消息要处理10s左右,那么这3个消息是被串行处理,在处理第一个消息的时候,后面的消息将被堵塞,同样反过来客户端也有同样的问题。
客户端Porcessor堵塞测试情况:
1.以下代码在建立连接后连续发送了5个消息(item)
?
 ?
?
ConnectFuture future = connector.connect(new InetSocketAddress(HOSTNAME, PORT));
future.awaitUninterruptibly();
session = future.getSession();
Item item = new Item();
item.setId(12345);
item.setName("hi");
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
2.在handle的messageSent方法进行了延时处理,延时3秒
?
 ?
?
public void messageSent(IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(message);
}
3.测试结果
5个消息是串行发送,都由同一个IoPorcessor线程处理
?????????????
 ?
?
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
session.write(item);
服务器端每隔3秒收到一个消息。因为调用是由IoProcessor触发,而一个connector只会使用一个IoProcessor线程
4.增加ExecutorFilter,ExecutorFilter保证在处理handler的时候是独立线程
connector.getFilterChain().addLast("threadPool", new ExecutorFilter(Executors.newCachedThreadPool()));
5.测试结果
4个session.wirte变成了并行处理,服务器端同时收到了5条消息