本文介绍Exchanger工具类, 然后采用Exchanger给出一个两个
线程交换数值的简单实例。
1. Exchanger介绍
class="java" name="code">/**
* A synchronization point at which two threads can exchange objects.
* Each thread presents some object on entry to the {@link #exchange
* exchange} method, and receives the object presented by the other
* thread on return.
*/
从上面的
注释中可以看出:Exchanger提供了
一个同步点,
在这个同步点,两个线程可以交换数据。每个线程通过exchange()方法的入口提供数据给另外的线程,并接收其它线程提供的数据,并返回。
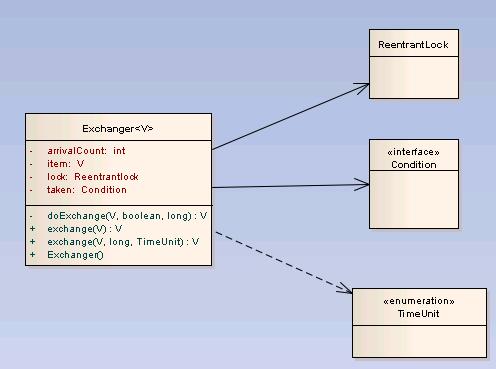
Exchanger通过Lock和Condition来完成功能,Exchanger的一个重要的public方法是exchange方法,用于线程的数据交换, 相关的类图以及详细的Exchanger类内容如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;
/**
* A synchronization point at which two threads can exchange objects.
* Each thread presents some object on entry to the {@link #exchange
* exchange} method, and receives the object presented by the other
* thread on return.
*
* <p><b>Sample Usage:</b>
* Here are the highlights of a class that uses an <tt>Exchanger</tt> to
* swap buffers between threads so that the thread filling the
* buffer gets a freshly
* emptied one when it needs it, handing off the filled one to
* the thread emptying the buffer.
* <pre>
* class FillAndEmpty {
* Exchanger<DataBuffer> exchanger = new Exchanger();
* DataBuffer initialEmptyBuffer = ... a made-up type
* DataBuffer initialFullBuffer = ...
*
* class FillingLoop implements Runnable {
* public void run() {
* DataBuffer currentBuffer = initialEmptyBuffer;
* try {
* while (currentBuffer != null) {
* addToBuffer(currentBuffer);
* if (currentBuffer.full())
* currentBuffer = exchanger.exchange(currentBuffer);
* }
* } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ... }
* }
* }
*
* class EmptyingLoop implements Runnable {
* public void run() {
* DataBuffer currentBuffer = initialFullBuffer;
* try {
* while (currentBuffer != null) {
* takeFromBuffer(currentBuffer);
* if (currentBuffer.empty())
* currentBuffer = exchanger.exchange(currentBuffer);
* }
* } catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ...}
* }
* }
*
* void start() {
* new Thread(new FillingLoop()).start();
* new Thread(new EmptyingLoop()).start();
* }
* }
* </pre>
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The type of objects that may be exchanged
*/
public class Exchanger<V> {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition taken = lock.newCondition();
/** Holder for the item being exchanged */
private V item;
/**
* Arrival count transitions from 0 to 1 to 2 then back to 0
* during an exchange.
*/
private int arrivalCount;
/**
* Main exchange function, handling the different policy variants.
*/
private V doExchange(V x, boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
lock.lock();
try {
V other;
// If arrival count already at two, we must wait for
// a previous pair to finish and reset the count;
while (arrivalCount == 2) {
if (!timed)
taken.await();
else if (nanos > 0)
nanos = taken.awaitNanos(nanos);
else
throw new TimeoutException();
}
int count = ++arrivalCount;
// If item is already waiting, replace it and signal other thread
if (count == 2) {
other = item;
item = x;
taken.signal();
return other;
}
// Otherwise, set item and wait for another thread to
// replace it and signal us.
item = x;
InterruptedException interrupted = null;
try {
while (arrivalCount != 2) {
if (!timed)
taken.await();
else if (nanos > 0)
nanos = taken.awaitNanos(nanos);
else
break; // timed out
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
interrupted = ie;
}
// Get and reset item and count after the wait.
// (We need to do this even if wait was aborted.)
other = item;
item = null;
count = arrivalCount;
arrivalCount = 0;
taken.signal();
// If the other thread replaced item, then we must
// continue even if cancelled.
if (count == 2) {
if (interrupted != null)
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return other;
}
// If no one is waiting for us, we can back out
if (interrupted != null)
throw interrupted;
else // must be timeout
throw new TimeoutException();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Create a new Exchanger.
**/
public Exchanger() {
}
/**
* Waits for another thread to arrive at this exchange point (unless
* it is {@link Thread#interrupt interrupted}),
* and then transfers the given object to it, receiving its object
* in return.
* <p>If another thread is already waiting at the exchange point then
* it is resumed for thread scheduling purposes and receives the object
* passed in by the current thread. The current thread returns immediately,
* receiving the object passed to the exchange by that other thread.
* <p>If no other thread is already waiting at the exchange then the
* current thread is disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of two things happens:
* [list]
* <li>Some other thread enters the exchange; or
* <li>Some other thread {@link Thread#interrupt interrupts} the current
* thread.
* [/list]
* <p>If the current thread:
* [list]
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@link Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting
* for the exchange,
* [/list]
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* @param x the object to exchange
* @return the object provided by the other thread.
* @throws InterruptedException if current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
**/
public V exchange(V x) throws InterruptedException {
try {
return doExchange(x, false, 0);
} catch (TimeoutException cannotHappen) {
throw new Error(cannotHappen);
}
}
/**
* Waits for another thread to arrive at this exchange point (unless
* it is {@link Thread#interrupt interrupted}, or the specified waiting
* time elapses),
* and then transfers the given object to it, receiving its object
* in return.
*
* <p>If another thread is already waiting at the exchange point then
* it is resumed for thread scheduling purposes and receives the object
* passed in by the current thread. The current thread returns immediately,
* receiving the object passed to the exchange by that other thread.
*
* <p>If no other thread is already waiting at the exchange then the
* current thread is disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of three things happens:
* [list]
* <li>Some other thread enters the exchange; or
* <li>Some other thread {@link Thread#interrupt interrupts} the current
* thread; or
* <li>The specified waiting time elapses.
* [/list]
* <p>If the current thread:
* [list]
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@link Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting
* for the exchange,
* [/list]
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then {@link TimeoutException}
* is thrown.
* If the time is
* less than or equal to zero, the method will not wait at all.
*
* @param x the object to exchange
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the <tt>timeout</tt> argument.
* @return the object provided by the other thread.
* @throws InterruptedException if current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws TimeoutException if the specified waiting time elapses before
* another thread enters the exchange.
**/
public V exchange(V x, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
return doExchange(x, true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
}
2. Exchanger工具类的使用案例
本文给出一个简单的
例子,实现两个线程之间交换数据,用Exchanger来做非常简单。
package my.concurrent.exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class ThreadA implements Runnable {
private final Exchanger<Integer> exchanger;
private final AtomicReference<Integer> last = new AtomicReference<Integer>(
5);
public ThreadA(Exchanger<Integer> exchanger) {
this.exchanger = exchanger;
}
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
last.set(exchanger.exchange(last.get()));
System.out.println(" After calling exchange. Thread A has value: " + last.get());
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package my.concurrent.exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class ThreadB implements Runnable {
private Exchanger<Integer> exchanger;
private final AtomicReference<Integer> last = new AtomicReference<Integer>(
10);
public ThreadB(Exchanger<Integer> exchanger) {
this.exchanger = exchanger;
}
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
last.set(exchanger.exchange(last.get()));
System.out.println(" After calling exchange. Thread B has value: " + last.get());
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package my.concurrent.exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
public class ExchangerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exchanger<Integer> exchanger = new Exchanger<Integer>();
new Thread(new ThreadA(exchanger)).start();
new Thread(new ThreadB(exchanger)).start();
}
}
运行一段时间之后的输出结果如下:
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 10
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread B has value: 5
After calling exchange. Thread A has value: 10
可以看出:两个线程的数据一直都在相互交换。
- 大小: 19.3 KB
